Next: The initial condition.
Up: The convection equation.
Previous: The convection equation.
The partial differential equation governing this problem for
s(x,t) is the convection equation or ``one-way wave equation'',
| 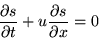 |
(6) |
It is an example of a hyperbolic equation. Unlike the parabolic
heat equation of the previous section, it allows singular solutions.
The one way wave equation also arises in much more general
one-dimensional unsteady hyperbolic problems by using standard
mathematical simplifications. For that reason, it is a very
important equation in the analysis of numerical schemes.
Next: The initial condition.
Up: The convection equation.
Previous: The convection equation.