Background
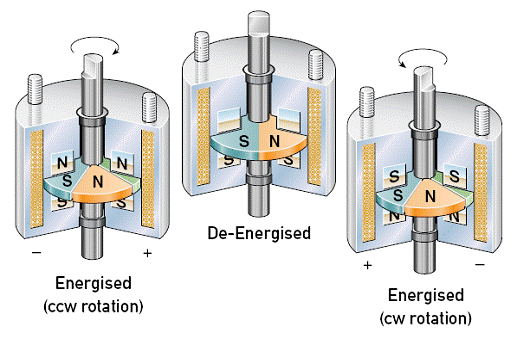
It is necessary to understand the principles of magnetism and electromagnetic motors in order to understand how a bi-directional rotary actuator works. Magnetism is one of the peculiar physical characteristics, which is caused by acts of the attractive or repulsive forces within a magnetic field. Magnetic fields can be seen where magnetic forces of magnetic dipoles are detected. It also occurs by electrical currents through wires because those electrical currents affect the others, which is called electromagnetism. Specifically, the motion of electrons produces magnetic field because every electron has a magnetic attribute. Magnetic force is calculated by cross product of electric charge, velocity of charged element, and magnetic field; Fleming’s left hand rule is applied to the force. In the rule, thumb, index finger, and middle finger indicate the direction of motion, field, and current respectively. The direction of the force is perpendicular to the magnetic field. Usually electromagnets are used for electromagnetism, which consists of a magnetic substance and coils wrapping around it. Iron, steel can be used as magnetic materials because magnets can attract those metals. When electric currents pass though the coils, the metal core is magnetized. The magnetized metal acts like a magnet, but the magnetic effect disappears when the current is not applied. The power of magnetic effect depends on the number of coils and the quantity of electrical current. By contrast, permanent magnets have magnetic attributes produced by the natural movement of electrons. Mainly mixtures of iron, cobalt, and nickel are used for permanent magnets.
In many fields, electromagnetism is used. An electric motor is one of the most important uses of magnets. It can switch electrical energy to mechanical energy. There are two types of electric motors: rotary and linear motors. The difference between two types of motors is the direction of movement based on how to assemble them. Also, an electrical motor can be classified by DC type and AC type. Among rotational actuators, a stepping motor has several advantages over other types of motors. It is able to position accurately because the degree per step of the rotary actuator can be controlled by the number of poles on a stator and permanent magnets on a rotor. Moreover, the rotary actuator can produce the highest torque at low speed. When currents are applied to a coil, poles on the stator are magnetized axially and magnetic field is formed. As magnetized poles act as electromagnets, they are in alignment with the opposite poles of the permanent magnet on the rotor by attracting them and repelling the same poles of the permanent magnet on the rotor. This procedure makes the rotor rotate in one direction with a specific angle. By the opposite direction of the current applied to the coil, the rotor will rotate in the other direction.