| Quantum Mechanics Solution Manual |
|
© Leon van Dommelen |
|
4.4.3.2 Solution esdb2-b
Question:
Continuing the previous question, evaluate the standard deviations in energy, square angular momentum, and 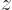 angular momentum in the 2p
angular momentum in the 2p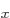 state using inner products.
state using inner products.
Answer:
For energy you have,
or multiplying out, noting that 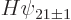

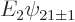 , so that
, so that 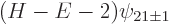
 0,
0,
which is zero. The same way, 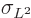
 0.
0.
For 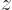 angular momentum, you have, since the expectation value is zero,
angular momentum, you have, since the expectation value is zero,
or multiplying out,
which multiplies out to 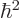 , so
, so 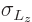 itself is
itself is 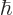 .
.
![]()
![]()
![]()