Fuel injection System
Nozzle Selection
Spray Nozzles
A nozzle is a
mechanical device that is designed to control fluid flow characteristics as
fluid, either liquid or gas, exits from an enclosed chamber into a chosen
medium. Nozzles are relatively simple in
design, usually a pipe or tube that varies in its cross-sectional area from one
end to another. Nozzles are used to
control different characteristics of fluid flow such as rate of flow,
direction, speed, mass, etc. Nozzles
also have the ability to control exit droplet size and fluid spray pattern,
which are the pertinent characteristics in this project.
Nozzle Selection
The following
characteristics are considered when selecting a nozzle: spray pattern,
capacity, spray angle, and droplet size. Spray pattern is dependent on the
function of the nozzle for its specific application. For the fuel jet injection
system a uniformly distributed spray pattern with a possible Gaussian
distribution is needed. Moreover, a relatively wide range of droplet sizes,
ranging from 500µm to 5000µm, need to be generated. Full cone spray nozzles
with different capacities (12-0.3 gpm) under different pressures (10-100psi)
can produce droplet sizes in the desired range.
Below
a tabulated summary is provided that contains different fluid properties and
nozzle characteristics and their effect on one another:
For
example; If there is an increase in the viscosity of the fluid
the associated "Nozzle Characteristic" is affected as indicated
by the indicated amount....
|
Nozzle
Characteristics
|
Increase in
Operating Pressure
|
Increase in
Specific Gravity
|
Increase in
Viscosity
|
Increase in
Fluid Temperature
|
Increase in
Surface Tension
|
|
Pattern Quality
|
Improves
|
Negligible
|
Deteriorates
|
Improves
|
Negligible
|
|
Drop Size
|
Decreases
|
Negligible
|
Increases
|
Decreases
|
Increases
|
|
Spray Angle
|
Increases then
decreases
|
Negligible
|
Decreases
|
Increases
|
Decreases
|
|
Capacity
|
Increases
|
Decreases
|
Full cone
increases
|
Depends on
fluid sprayed
and nozzle used
|
No effect
|
|
Impact
|
Increases
|
Negligible
|
Decreases
|
Increases
|
Negligible
|
|
Velocity
|
Increases
|
Decreases
|
Decreases
|
Increases
|
Negligible
|
|
Wear
|
Increases
|
Negligible
|
Decreases
|
Depends on
fluid sprayed
and nozzle used
|
No effect
|
Table 1: (Spraying Systems Co., [1])
There are many
terminologies used to describe the drop sizes within a spray; three of the most
commonly used terminologies are:
- Volume Median Diameter (VMD) also expressed as Dv0.5
and Mass Median Diameter (MMD)
Drop size is
expressed in terms of the volume of liquid sprayed, and when measured in terms
of volume is a value with 50% of total volume of liquid sprayed contains drops
with diameters larger than median value and 50% with smaller diameters.
- Sauter Mean Diameter (SMD) also shown as D32
Fineness of spray
is expressed in terms of surface area produced by the spray. SMD is the
diameter of a drop with the same volume-to-surface area ratio as the total
volume of all the drops to the total surface area of all the drops
- Number Median Diameter (NMD) or DNo. 5
Drop size is
stated as the number of drops in the spray. So, 50% of the drops by count or
number are smaller than the median diameter and 50% are larger than the median
diameter.
Volume Median
Diameter or VMD is the most popular known expression used to represent drop
size distribution in most nozzles.
Final selection of the nozzle is
done by examining a graph provided by the manufacturer of the nozzle that gives
spray particle size in VMD versus pressure for standard full cone nozzles. The
graph is done for many nozzles with different capacities. It is very important
to mention that these tests were done for water and the particle size provided
is for water at room temperature. The graph is only used to aid us through
selecting the correct nozzle, but is in no case the final nozzle
characterization. The actual characterization of the nozzle will be done by us.
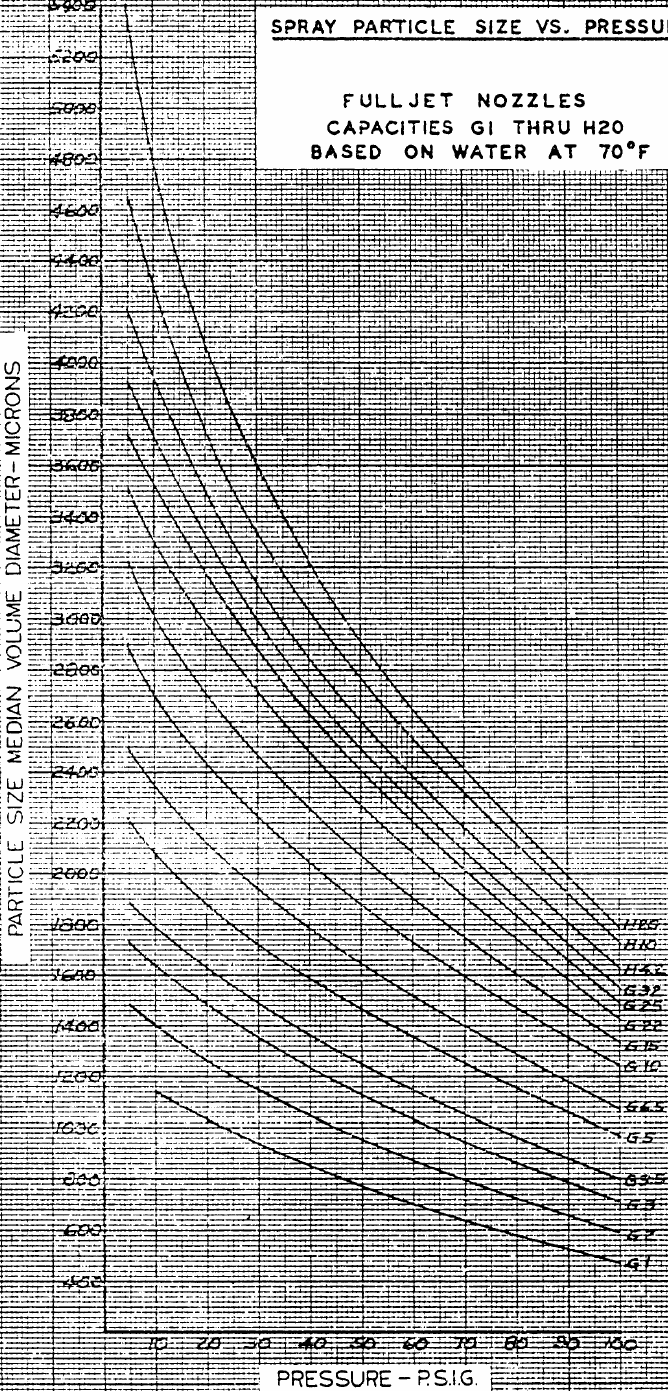
"Nozzle Selection, graph spray particle
versus pressure (Spraying Systems Co,[2])"
The actual nozzles
selected from Spraying Systems Company are the following:
Table 2- nozzle selection
|
Order number
|
Nozzle type
|
Capacity size
|
Material
|
Inlet Connection
|
Thread type
|
(VMD of water)
|
Pressure range for
VMD
|
|
1/8G-316SS1
|
G
|
1
|
316 Stainless steel
|
1/8”
|
Female NPT
|
500-1000µm
|
120-10psi
|
|
1/8G-316SS3.5
|
G
|
3.5
|
316 Stainless steel
|
1/8”
|
Female NPT
|
1000-1700 µm
|
90-
10psi
|
|
3/8G-316SS15
|
G
|
15
|
316 Stainless steel
|
3/8”
|
Female NPT
|
1500-3000µm
|
100-10psi
|
|
2-1/2H-SS25
|
H
|
25
|
316 Stainless steel
|
2-1/2”
|
Female NPT
|
2000-5000 µm
|
90-
5psi
|
REFERENCES
[1] Nozzle selection, table 1:
Spraying Systems Co., Engineers
Guide to Spray Technology, Page 8, year 2000
[2] Nozzle Selection, graph spray particle
versus pressure
Spraying Systems Co., DWG. No.
11825-8 ,Bellwood ILL, Sept. 27, 1966
|




