Electrical Design
Electrical setup includes two power supply and circuit box
The data acquisition board (DAQ) will be connected to several instruments as shown below: it will record data from the slip rings, receive pulses from the encoder, measure the magnetic field generated by the magnet, and control the motor, via a motor drive
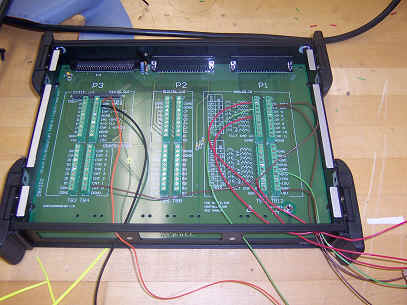

DAQ board and design schematic
Data from the slip rings will be preprocessed using physical integrators. Their role is to integrate the raw voltage generated by the coil. Therefore, the output voltage from the integrators is proportional to flux magnitude. This value is measured directly by the DAQ board.
The encoder provides information about the position of the shaft: 1024 pulses are generated for each revolution. These pulses are used to trigger the DAQ board; therefore flux will be measured at fixed angles of the shaft's rotation.
Magnetic field readings will be taken at the beginning of each measurement set, and will provide a reference for the evaluation of the performance of the rotating shaft measurement system (the slip rings in particular).
 A motor controller, connected to the DAQ board is used
to adjust motor speed. There are therefore two power supplies, one for the
motor, and one for certain electronic components of the circuit; ultimately, the DAQ board will send all the
signals to a desktop computer running LabVIEW software that will interpret
these signals. The figure to the left shows the data acquisition hardware
within a circuit box and the emergency shut of system that will automatically
shut down the test if any problems arise while the test is running. This
box is located at an appropriate distance away from the test assembly to ensure
that the system is easily shut off in an emergency situation.
A motor controller, connected to the DAQ board is used
to adjust motor speed. There are therefore two power supplies, one for the
motor, and one for certain electronic components of the circuit; ultimately, the DAQ board will send all the
signals to a desktop computer running LabVIEW software that will interpret
these signals. The figure to the left shows the data acquisition hardware
within a circuit box and the emergency shut of system that will automatically
shut down the test if any problems arise while the test is running. This
box is located at an appropriate distance away from the test assembly to ensure
that the system is easily shut off in an emergency situation.
More information concerning the data acquisition and analysis of the system can be found on the software design page


Clockwise from the left: Integrator circuit, circuit box, Motor controller circuit