This section includes a summary of the final design as well as pictures of each
component and diagrams that will illustrate how the system works.

Subassembly Components
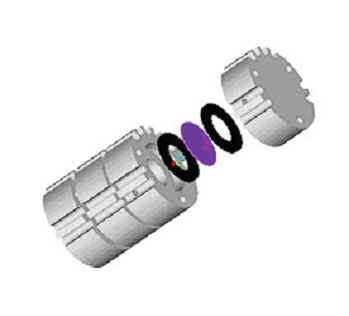
The figures below show CAD images of the individual components of the
subassembly as well as an exploded view of the subassembly including the fuel
cell and gaskets. Each subassembly component will be machined out of alumina
silicate purchased from Cotronics, Inc.
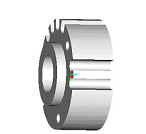
Each component of the subassembly includes a set of grooves along the outer
perimeter to accommodate the gas inlet and outlet tubes. Each compartment is
sealed from its neighbor by the combination of the fuel cell and the vermiculite
gasket on either side as seen below.
The figures below show an enlarged view of the connection between the gas
inlet tubing and the subassembly as well as an exploded view of how the gaskets
interact with the fuel cell and
subassembly.
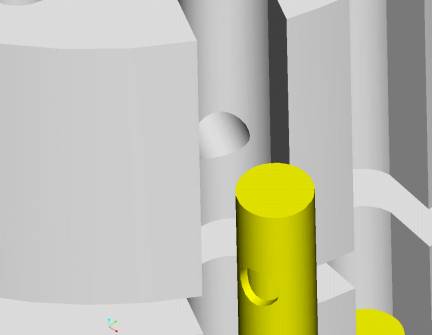
Connection between gas tubing and subassembly
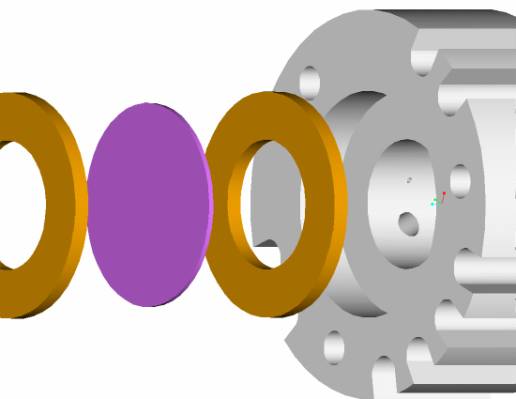
Interaction
between gaskets, fuel cell, and subassembly component
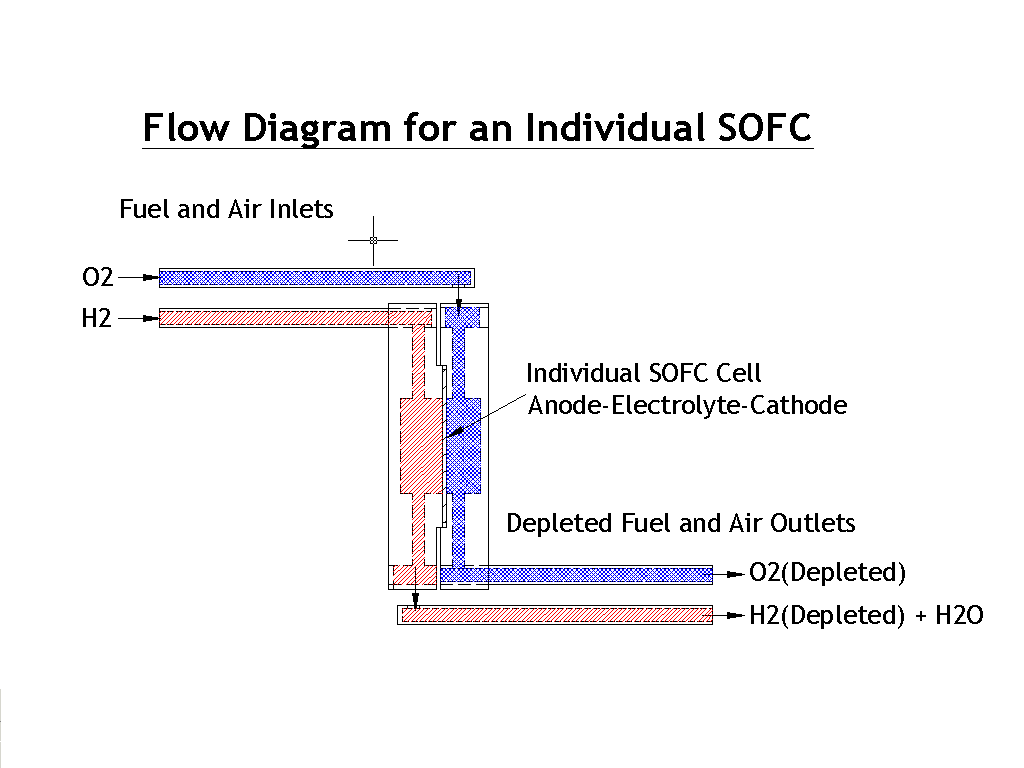
Gas Flow
The gas flow in our system has been simplified from the original idea of
perpendicular flow. This new design has the gas flows entering and exiting along
the main axis of the subassembly. A diagram of the gas flow in an individual
component is shown below.
Heating Component
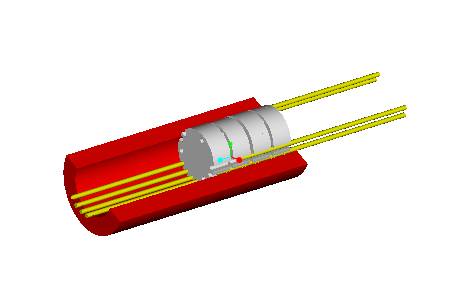
The subassembly rests in one end of a cylindrical ceramic heater and the
additional space in the heater is used to heat the incoming gas flows. The
incoming hydrogen and oxygen flows come in near the bottom surface of the heater
while the exhaust flows exit the heater near the sidewalls. The heating setup is
shown below.
Insulation and Housing
The heater and subassembly will be insulated using alumina bricks from
Cotronics, Inc. When the heater is at operating temperature, the insulation will
allow the system to be safely handled as the surface of the bricks will only
become warm to the touch. The whole system will rest inside of an outer housing
unit. The housing unit aides in the mobility and containment of our test
facility.







