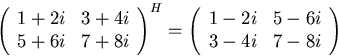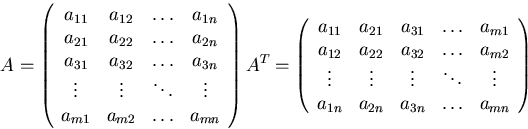
Transposing a matrix turns the columns into rows and vice-versa
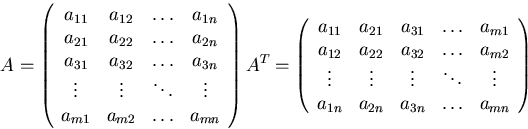
Another way of thinking about it is that the elements are flipped over around the ``main diagonal'', which runs from top left to bottom right:
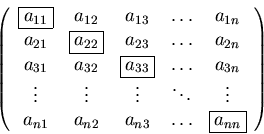
Note that ![]() .
.
Transpose in index notation:
![]()
Note that in index notation, the main diagonal consists of the elements where i=j. These stay put during transposing.
Transposing matrix products:
(AB)T = BT AT
For complex matrices, the normal generalization of transpose is
``Hermitian conjugate'', where you take the complex conjugate of each
complex number, in addition to interchanging rows and columns:
![]() , or
, or ![]() .
.
Example: